SK Loops
The reason SK Loops are in the 'diabolical' strategies and not the 'extreme' as this is quite a stand-out pattern. However, it was discovered (invented?) trying to solve the Easter Monster and it requires a crowded field of candidates, which is typical of the very hardest puzzles.
Credits first: I'm indebted to pjb or Phil from Sydney, Australia for his write up here and the many examples he's collected on his website here. The solver will find SK Loops for all Phil's types from the vanilla down to Type H, but not as yet "Related Loops". In my implementation I don't discern 'types' as I've generalized the detection. SK Loops are apparently a subset of something larger but I've not explored this yet.
Credits first: I'm indebted to pjb or Phil from Sydney, Australia for his write up here and the many examples he's collected on his website here. The solver will find SK Loops for all Phil's types from the vanilla down to Type H, but not as yet "Related Loops". In my implementation I don't discern 'types' as I've generalized the detection. SK Loops are apparently a subset of something larger but I've not explored this yet.
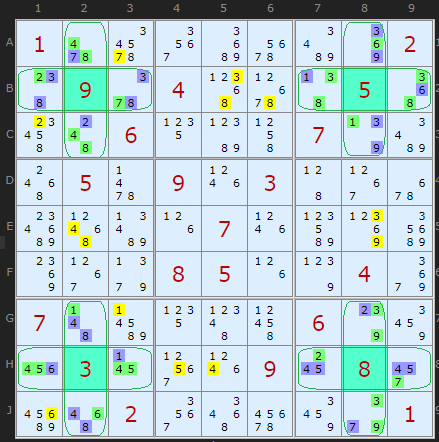
I'm going to start, as Phil does, with the Easter Monster, since the pattern is nicely spread out and symmetrical. SK Loops are bi-directional continuous loops meaning that the loop can be started at any point and you can trace the links in either direction.
First find four solved or given cells spread over four boxes such that they make a rectangle. Phil distinguishes between givens (clues) and solved cells but I do not and I've not found a false positive because of this.
Shown in the diagram are four such numbers and surrounding them are eight 2-cell pairs containing Hidden Pairs
The pattern definition is then
Now, the pattern definition requires sum of the links is less than or equal to 16. To see what we are counting, here is the formal definition of the loop
(27=38)B13- (38=16)B79- (16=39)AC8- (39=27)GJ8- (27=45)H79- (45=16)H13- (16=48)GJ2- (48=27)AC2-
The solver always starts at the top-left most given cell and the row and loops clockwise, so pair B13 starts. (Phil's starts in a different place in his documentation). B13 is Strongly Linked to B79 on the Hidden Pair {3,8}. Looking at all the links and counting the candidates in each pair we get
Since we have identified the content of these sixteen cells as a Locked Set we can eliminate along the unit of alignment. So, since B13 contains a blue {3,8} and B79 contains a green {3,8} and the solution will be one or the other, so we can remove 3 and 8 from B5 and B6.
- The loop requires 4 boxes in 2 bands and and 2 stacks, and 8 links, one link in each box, one link in each row and one link in each column.
- In each box the cell at the intersection of the row cells and column cells is a given.
- Loops can include single, double or triple links, as long as the sum of the links is less than or equal to 16.
- Of the 2 cells involved in a row or column within a box, one of the two can be solved, but not a given.
Now, the pattern definition requires sum of the links is less than or equal to 16. To see what we are counting, here is the formal definition of the loop
(27=38)B13- (38=16)B79- (16=39)AC8- (39=27)GJ8- (27=45)H79- (45=16)H13- (16=48)GJ2- (48=27)AC2-
The solver always starts at the top-left most given cell and the row and loops clockwise, so pair B13 starts. (Phil's starts in a different place in his documentation). B13 is Strongly Linked to B79 on the Hidden Pair {3,8}. Looking at all the links and counting the candidates in each pair we get
SK Loop Type 2-2-2-2-2-2-2-2-
and those numbers add up to 16.Since we have identified the content of these sixteen cells as a Locked Set we can eliminate along the unit of alignment. So, since B13 contains a blue {3,8} and B79 contains a green {3,8} and the solution will be one or the other, so we can remove 3 and 8 from B5 and B6.
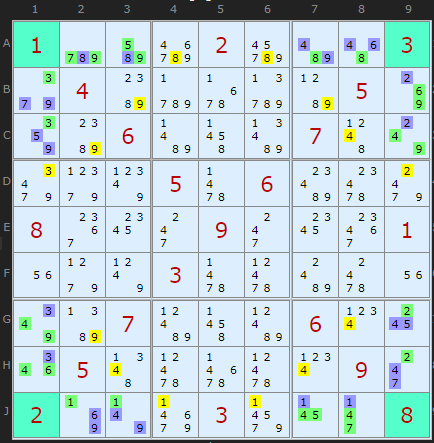
This SK Loop alternates Triple and Single links instead of the classic doubles all round. This makes the type 3-1-3-1-3-1-3-1- but those numbers still add up to 16.
Take a moment to trace some of the links in the diagram and compare to the definition of the loop:
(579=8)A23- (8=469)A78- (469=2)BC9- (2=457)GH9- (457=1)J78- (1=469)J23- (469=3)GH1- (3=579)BC1-
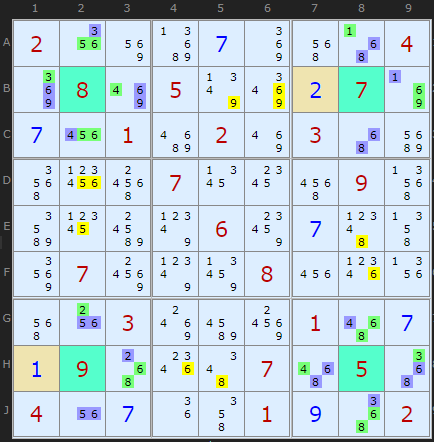
Lastly we can consider the fourth element of the SK Loop definition, the cases where one of the two cells in a pair is a solved cell. Phil states this cannot be a given, but I am still searching for a counter example and the solver does not distinguish.
The type for this loop, 2-2-1-2-2-2-1-2- now adds up to only 14, which is correct since two of the cells (colored in beige) have been used up.
(34=69)B13- (69=1)B79- (1=68)AC8- (68=34)GJ8- (34=68)H79- (68=2)H13- (2=56)GJ2- (56=34)AC2-
Exemplars
I won't duplicate the excellent list provided by Phil on his help page here.

Comments
Email addresses are never displayed, but they are required to confirm your comments. When you enter your name and email address, you'll be sent a link to confirm your comment. Line breaks and paragraphs are automatically converted - no need to use <p> or <br> tags.
... by: Visitor
I understand the loop:
In the first box,
green 3 & blue 3 together with green 4 & blue 4 build two pairs (in A2,B1,B3 & C2),
same for the last box,
where green 3 & blue 3 together with green 4 & blue 4 build two pairs (in G8,H7,H9 & J8),
whereas in the third box
the green 1 in A8 and the blue 1 in B9 do not build two pairs together with a green 2 and a blue 2, but together with the solved 2 in B7
and in the seventh box
the green 2 in G2 and the blue 2 in H3 do not build two pairs together with a green 1 and a blue 1, but together with the solved 1 in H1
What I do not understand is the eliminations in rows B and H.
In row B
based on the assumption that green is ON, you need the eliminated digits to build a triple in the fields B5, B6 & B9 containing of the green 1, 6 & 9
In row H
based on the assumption that green is ON, you need the eliminated digits to build a triple in the fields H3, H4 & H5 containing of the green 2, 6 & 8
Anybody has an explanation for me on this? Thank you!
... by: Kyrie Iris
SK Loops and Twinned XY-Chains is subsets of this.
The conditions are the following three:
1. Place candidates in each column, row, and box. Candidates of the same type are allowed. The cell at their intersection contains only that candidates.
2. In each column, row, and box, if number of candidates in one unit is n, number of intersectrion cells in the unit must be n + 1 or more. If there are not, you need to add cells on that unit.We call these 'escape cell'. The escape cells must contain only the candidates in the unit. If there are too many intersection cells, they may be subject to deletion for reasons described in condition 3..
3. The number of intersections and escape cells must be the total number of all candidates (including duplicates). If there are not enough, add escape cells.If there are too many, remove some intersection cells. However, do not remove escape cells. Also, if there is only one type of candidate in one intersection cell, remove the intersection cell.
If these conditions are satisfied, the candidates placed in each column, row, and box can be removed from the other cells in the unit.
I call this Extended XY-Chains (EXY), and if 'the total number of intersections and escape cells' = 'the total number of all candidates' is N, I write this as EXY(N).
I'm sorry that I can't make a specific example for this. But a simple candidates layout can be quickly created:
for example,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
A {2,5,6} {3,5,6} {4,5,6} {2,4,7,6}
B
C
D {3,8} {2,7,8}
E
F
G {1,2} {1,3} {1,2,7}
H
J
A6 is escape cell.Total number of candidates = total number of cells is 9. The condition 1.2.3.of EXY are satisfied. By EXY 2,3,{2,7} can be removed from column1,4,9, and {4,5,6},8,1 can be removed from rowA,D,G.
In the case of Easter Mosnters, Box1 is {2,7},Box3 is {1,6}, Box7 is {1,6}, Box9 is {2,7}, and column 2 is {4,8}, column 8 is {3,9}, rowB is {3,8}, rowH is {4,5}. Total number of candidates = total number of cells is 16.The condition 1.2.3.of EXY are satisfied.
[Proof]
Prove it by mathematical induction.
(i) We need to consider the minimal possible pattern.This is the case when the number of candidates = the total number of cells is 4(N=4). In this case, condition 1.2.3. is satisfied by XY-Chains or two Locked Sets, and EXY(4) elimination rule is clearly true. For example, XY-Chains are {1,2},{2,3},{3,4},{4,1}, and Locked Sets are {1,2},{1,2},{3,4},{3,4}, etc.
(ii) Let 'number of candidates' = 'number of cells' = N > 4, and assume that EXY holds for N − 1 or less. Let us arbitrarily choose one intersection cell and assume that one of the candidates will be placed in it.Then,one number of candidates and cells in the unit to which the candidate belongs decreases by one, so condition 2. is satisfied.When we look at another unit to which that candidate belongs, the number of candidates does not decrease, but the number of cells decreases by one, so the number of cells in the unit may be equal to or greater than the number of candidates.
(a) If 'Number of cells'>'Number of candidates', focusing on the remaining cells, condition 1.2.3. holds for N − 1 candidates and N − 1 cells, so by induction assumption EXY(N − 1) holds. Therefore, EXY(N) holds, including the candidate selected initially.
(b) If 'Number of cells'='Number of candidates', remove them and consider the next step. Then, in the other unit removed cells belonged to, the number of candidates will not decrease, but only the number of cells will decrease, so this also means that the number of cells may be equal to or greater than the number of candidates (although it may never be less due to escape cells?).By repeating this operation, only those whose number is greater than the number of candidates remain.
Since the number of cells is finite, this operation can be completed a finite number of times. If the number of cells removed is m, then N−1−m candidates and N − 1 − m cells remain, and condition 1.2.3. is satisfied, so by induction assumption EXY(N − 1 − m) is satisfied.
Now, let’s look at the cells that were removed. The group of cells removed in the last operation has a unit in common with the previous EXY(N − 1 −m). Therefore, all candidates that belong to that unit are removed from the group of cells by that EXY. Then, since the number of cells is equal to the number of candidates, it becomes a Locked Set. If the number of candidates that are determined by this is k, then EXY(N −1−m+k) holds again.
Furthermore, the same can be said for the group of cells removed in the one more previous step, so by repeating this operation a finite number of times, it is possible to confirm that EXY(N − 1) holds. EXY(N) holds together with the initially selected candidate.
According to (a) and (b), if we try all possible candidates within the initially selected cell, we can see that EXY(N) holds in all cases.
Therefore, if EXY holds for N − 1 or less, then EXY(N) holds even when N.
(Q.E.D.)
...1.........2.3...4........5.....6........7.8...9
A{2,5,6}........{3,5,6}......{4,5,6}........{2,4,7,6}
B
C
D..................{3,8}............................{2,7,8}
E
F
G{1,2}..........{1,3}............................{1,2,7}
H
J
In (i) of the proof by mathematical induction, I said that the minimal pattern was N=4, but N=1, 2, and 3 also exist.
N=2 and 3 are Locked Set. N=1 is the case where a single cell contains one candidate, which does not strictly satisfy condition 2.. However, for convenience we will also consider this as EXY(1).
... by: Anonymous
All 16 digits are restricted commons, meaning each digit can only upto 1 time in the loop. Now the 16 cells should have 16 digits, so each of the 16 restricted commons should appear exactly once, which explains the eliminations.
And yeah, as I said, the givens/solved cells don't seem to be important.
... by: Anonymous
... by: Robert
I think I have figured out the logic of the SK loop,and how the eliminations take place. But the description has an issue - it is not a matter of all the blue being true or all the greens being true - in fact, in the easter monster puzzle, this is not the case.
Starting at B13, if {3,8} is "true" so that the two cells contain these two values, this propagates all the way around the chain, making all of the blue candidates true. And if {2,7} is "true", this also propagates all the way around (the other direction), and makes all of the green candidates true.
But these are not the only two possibilities. B13 could contain one of {3,8} and also one of {2,7}, and in fact this is what happens in the unique solution. But we still get the eliminations in this case. Suppose there is no "3" in B13 or B79. Then if B13 also contains no "8", it must contain {2,7}, and all the green candidates are "true", including the {3,8} in B79 - this contradicts the assumption that B79 contains no "3". So B13 must contain an "8", meaning B79 cannot. But then B79 does not contain a "3" and does not contain an "8", so it must contain the blue candidates, so that all the blue candidates are true, including {3,8} in B13. So this is also contradictory. So if B13 and B79 do not contain a "3", B13 containing no "8" results in a contradiction, and B13 containing an "8" also results in a contradiction - therefore, B13 or B79 must contain a 3. By the analogous reasoning, B13 and B79 must contain an "8". However, it does not have to be the same group - in the unique solution, it is B13 that contains the "3", and B79 that contains the "8".
So I understand how the loop works now, but the description, which says that all the blue are true or all the green are true, is not correct. It's more subtle than that.
... by: Robert
It doesn't seem like the comments are monitored closely, but I'll try anyway.
I am really struggling to understand how SK loops work, and the link to pjb's comments isn't helping that much - it seems to presume some knowledge of the technique already.
From the description of the Easter Monster on this page, we have:
"Since we have identified the content of these sixteen cells as a Locked Set we can eliminate along the unit of alignment. So, since B13 contains a blue {3,8} and B79 contains a green {3,8} and the solution will be one or the other, so we can remove 3 and 8 from B5 and B6."
I am interpreting this to mean that either (i) all the blue candidates are "true" and all the green candidates are "false", or (ii) all the blue candidates are "false" and all the green candidates are "true". But according to the solution count" feature in the solver, B1 should be 2 (which is green) and B3 should be 3 (which is blue).
So am I misunderstanding something, or is there something wrong with the description?